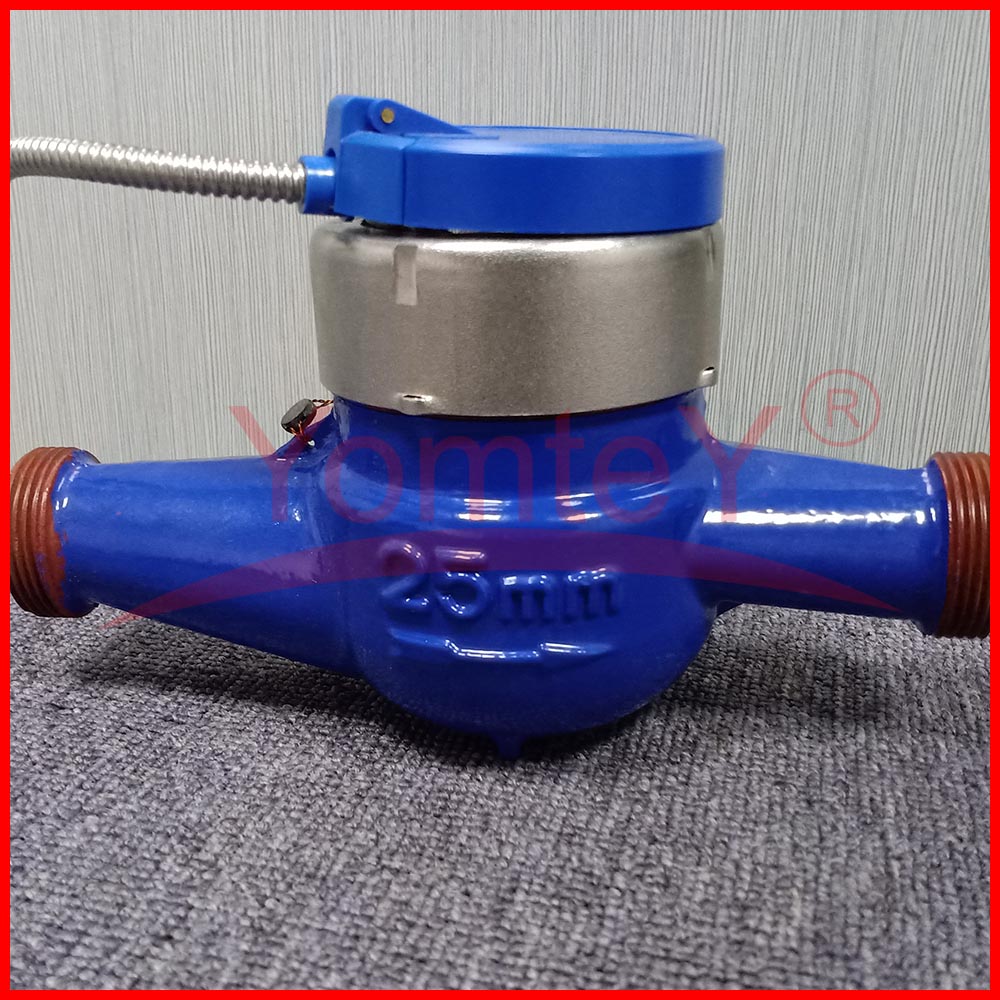
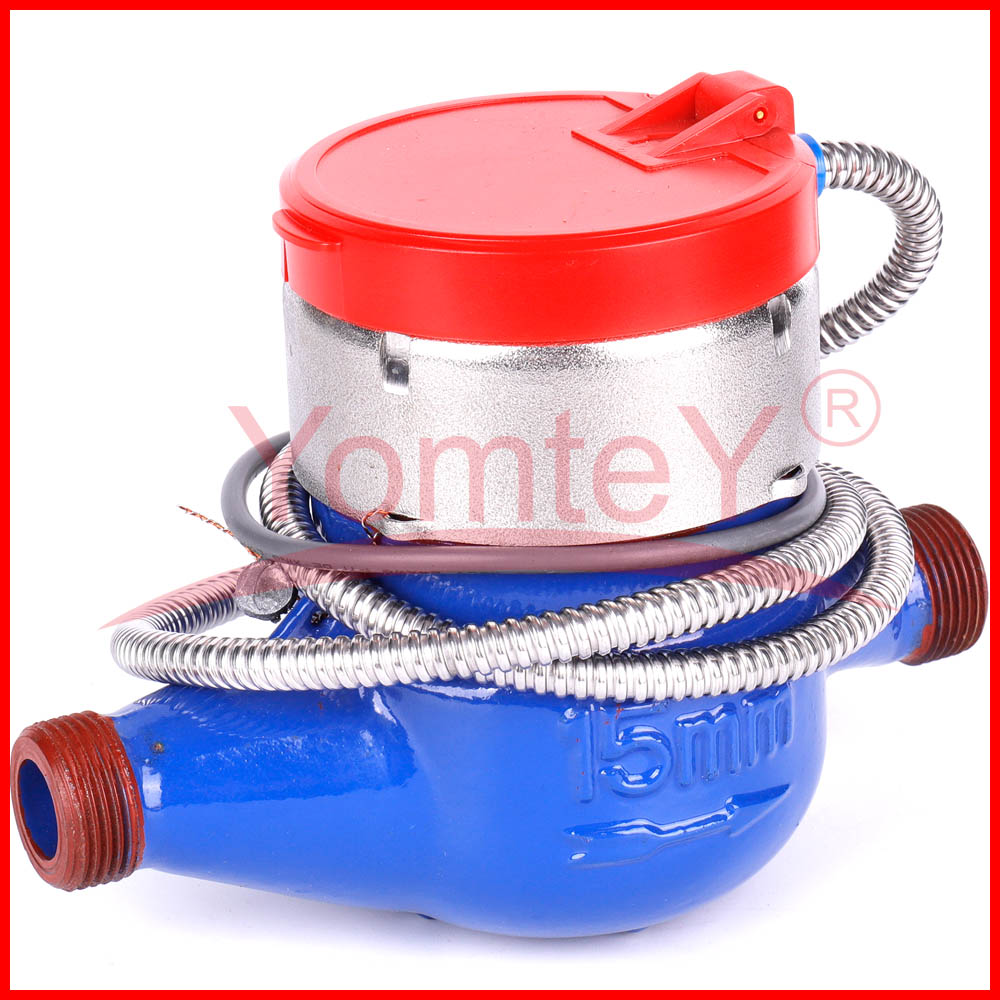
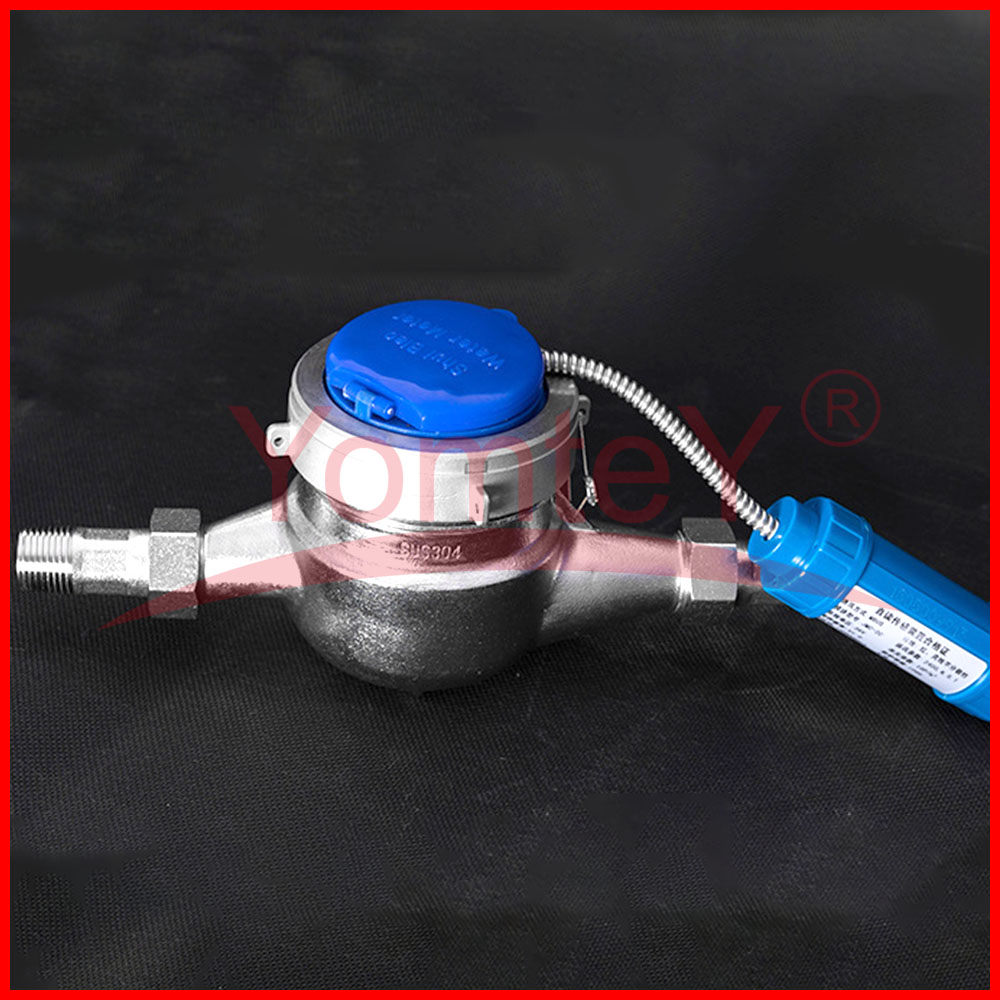
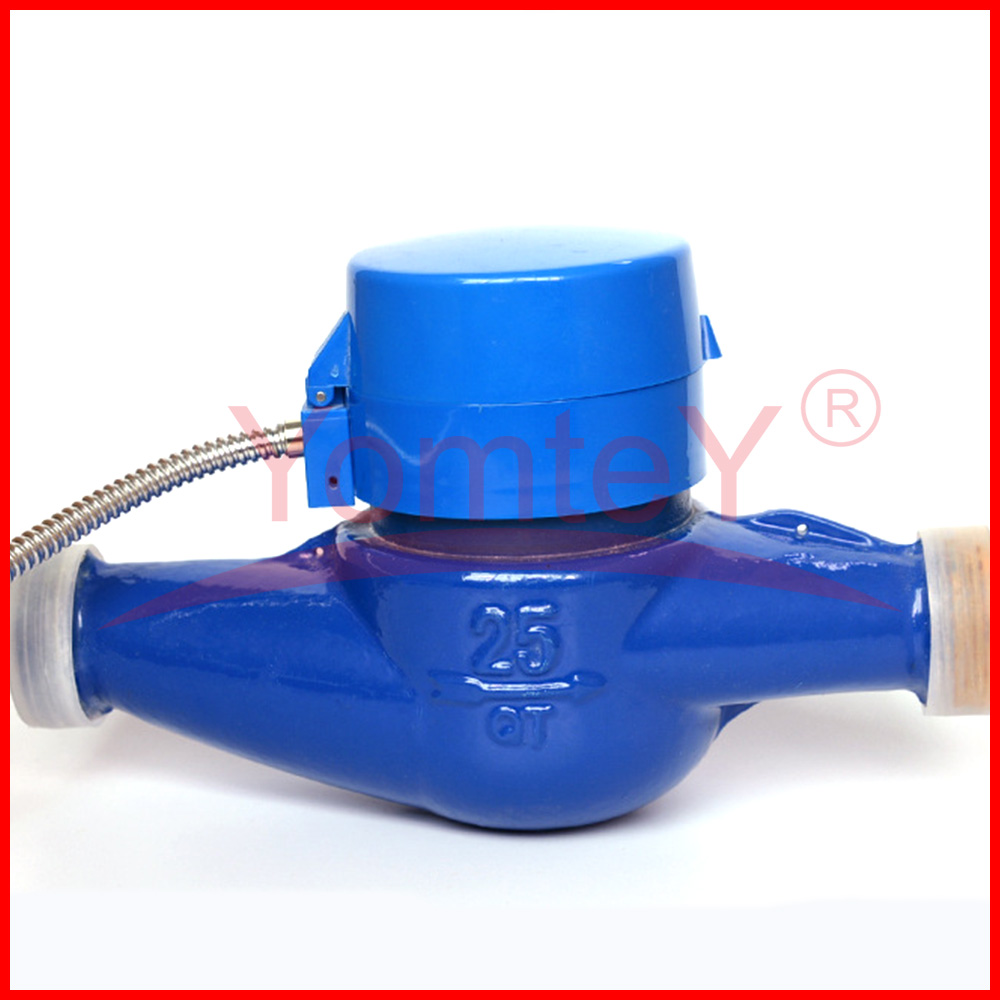
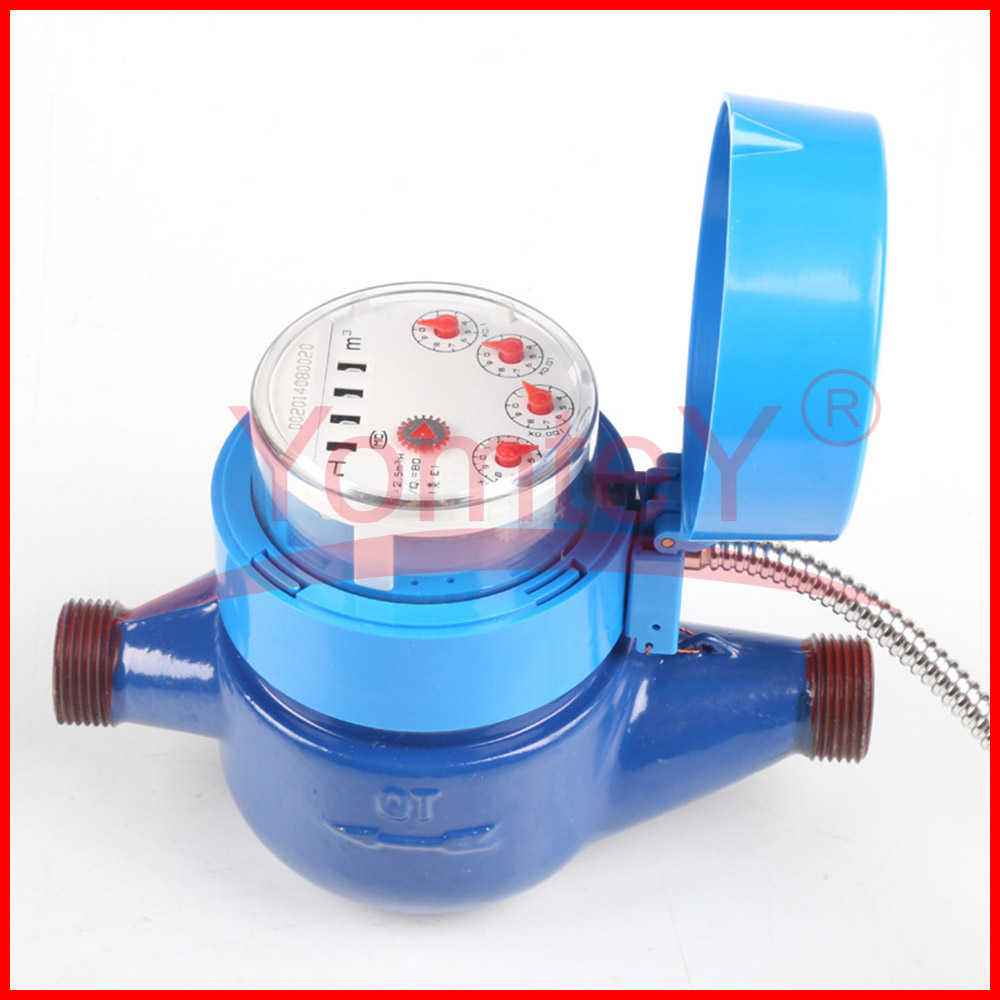
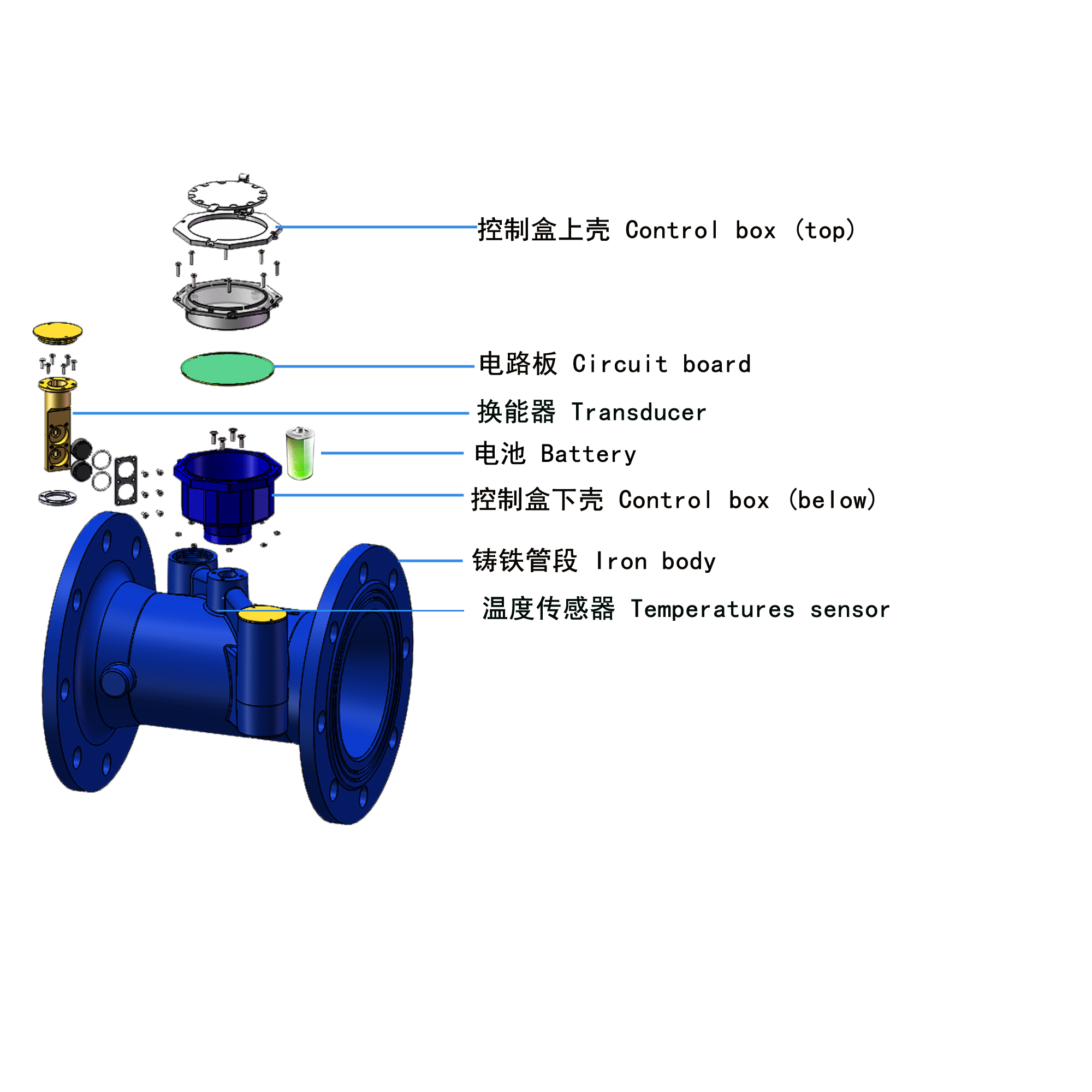
YomteY provides custom intelligent water meter as your request. The M-Bus interface is made for communication on two wires, making it cost-effective. A radio variant of M-Bus (Wireless M-Bus) (circle-link) is also specified in EN 13757-4. Intelligent water meter is a new type of water meter that uses modern microelectronic technology, modern sensing technology, and intelligent IC card technology to measure water consumption, transfer water consumption data and settle transactions. Compared with the traditional water meter, which only has the function of flow collection and a mechanical pointer to show the water consumption, it is great progress.
In addition to recording and electronic display of water consumption, intelligent water meters can also control water consumption in accordance with the contract, and automatically complete the calculation of water price at the step level. At the same time, they can store water consumption data.
Advantage of smart water meter:
1. Water consumption can be recorded and displayed electronically;
2. The water consumption can be controlled in accordance with the agreement, and the calculation of water price at the ladder price can be automatically completed, and the water consumption data can be stored;
3. Data transfer and trading settlements are carried out through an IC card, which features convenient trading, accurate calculation and bank settlement.
What is the difference between M-Bus and Modbus ?
M-Bus (Meter-Bus) is a European standard (EN 13757-2 physical and link layer, EN 13757-3 application layer) for the remote reading of gas or electricity meters. M-Bus is also usable for other types of consumption meters. The M-Bus interface is made for communication on two wires, making it cost-effective. A radio variant of M-Bus (Wireless M-Bus) is also specified in EN 13757-4.
The M-Bus was developed to fill the need for a system for the networking and remote reading of utility meters, for example, to measure the consumption of gas or water in the home. This bus fulfills the special requirements of remotely powered or battery-driven systems, including consumer utility meters. When interrogated, the meters deliver the data they have collected to a common master, such as a hand-held computer, connected at periodic intervals to read all utility meters of a building. An alternative method of collecting data centrally is to transmit meter readings via a modem.
Modbus is a serial communications protocol originally published by Modicon (now Schneider Electric) in 1979 for use with its programmable logic controllers (PLCs). Modbus has become a de facto standard communication protocol and is now a commonly available means of connecting industrial electronic devices. The main reasons for the use of Modbus in the industrial environment are:
developed with industrial applications in mind,
openly published and royalty-free,
easy to deploy and maintain,
moves raw bits or words without placing many restrictions on vendors.
Modbus enables communication among many devices connected to the same network, for example, a system that measures temperature and humidity and communicates the results to a computer. Modbus is often used to connect a supervisory computer with a remote terminal unit (RTU) in supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems. Many of the data types are named from its use in driving relays: a single-bit physical output is called a coil, and a single-bit physical input is called a discrete input or a contact.
The development and update of Modbus protocols have been managed by the Modbus Organization since April 2004, when Schneider Electric transferred rights to that organization. The Modbus Organization is an association of users and suppliers of Modbus-compliant devices that advocates for the continued use of the technology.
RS-485 supports inexpensive local networks and multidrop communications links, using the same differential signaling over twisted pair as RS-422. It is generally accepted that RS-485 can be used with data rates up to 10 Mbit/s[a] or, at lower speeds, distances up to 1,200 m (4,000 ft). As a rule of thumb, the speed in bit/s multiplied by the length in meters should not exceed 108. Thus a 50-meter cable should not signal faster than 2 Mbit/s.
In contrast to RS-422, which has a driver circuit which cannot be switched off, RS-485 drivers use three-state logic allowing individual transmitters to be deactivated. This allows RS-485 to implement linear bus topologies using only two wires. The equipment located along a set of RS-485 wires is interchangeably called nodes, stations or devices. The recommended arrangement of the wires is as a connected series of point-to-point (multidropped) nodes, i.e. a line or bus, not a star, ring, or multiply connected network. Star and ring topologies are not recommended because of signal reflections or excessively low or high termination impedance. If a star configuration is unavoidable, special RS-485 repeaters are available which bidirectionally listen for data on each span and then retransmit the data onto all other spans.
Typical bias network together with termination. Biasing and termination values are not specified in the RS-485 standard.
Ideally, the two ends of the cable will have a termination resistor connected across the two wires. Without termination resistors, signal reflections off the unterminated end of the cable can cause data corruption. Termination resistors also reduce electrical noise sensitivity due to the lower impedance.[further explanation needed] The value of each termination resistor should be equal to the cable characteristic impedance (typically, 120 ohms for twisted pairs). The termination also includes pull up and pull down resistors to establish fail-safe bias for each data wire for the case when the lines are not being driven by any device. This way, the lines will be biased to known voltages and nodes will not interpret the noise from undriven lines as actual data; without biasing resistors, the data lines float in such a way that electrical noise sensitivity is greatest when all device stations are silent or unpowered.
YomteY creates beautiful products for city builders worldwide.
| Category | Remote Reading Water Meter |
| Size | DN10 – DN500 |
| Material | Brass/Plastic/Stainless Steel |
| Brand Name | YomteY |


Trust worthy AMR water meters manufacturer
How to Place An Order =======
Click the “Send EMail” button below.
Send your drawing and specification to us.
Check the response and help us to confirm the details.
Check the quotation & invoice you received and confirm the price.
Arrange the prepayment and waiting for the delivery time we agreed on the quotation.
YomteY arranges the shipment and inform you the tracking message, waiting for your feedback and next cooperation.
What Client Say
Thank you very much.
The water meters are perfect and they fit good.
“We received our order today and just wanted to let you know that you met our hopes for the quality of the parts. The customer service and support on this first order were excellent! Thank you!
We are a professional manufacturer of RS485 water meters
Durable Meter helps you deal well with your project problem.
Fast responsive so your design will always be treated seriously and come true very soon!





